Swot Analysis
Concept utility.
SWOT analysis is a framework tool to help you assess your firms strategic options to achieve your desired goals and objectives.
History.
The acronym SWOT stands for Strength Weakness Opportunity Threat analysis, and is attributed to Albert Humphrey the management consultant and HBS grad who led a convention at the Stanford Research Institute throughout the 60s and 70s analyzing data from Fortune 500 firms. Humphrey was also notable for his association with the Stakeholder Concept as well as setting the scene for the Investors in People scheme. The purpose of the SWOT analysis is to assess the strategic landscape alongside the advantages and disadvantages from within the company itself.
Explanation.
A SWOT analysis is one way of visualizing the strategic choices available to a company. It is commonly laid out in a 2×2 matrix, with helpful and harmful broken down along one side of the square and external and internal along the other. Strengths appear in the top left quadrant, weaknesses in the top right, opportunities in the bottom left corner and threats in the bottom right. The purpose of this framework is to map the company’s assets and Achilles’ heel and also to set the context of the market in which it operates. The SWOT analysis will allow realistic goals to be set for the company in question.

Strengths are aspects of your business which give you an advantage over your competitors or potential competitors. These aspects should arise from the capabilities emergent from within your firm rather than beneficial, external trends.
Weaknesses are facets of your company which may prove a hindrance to your operation or strategic potential in the future. These are aspects may place you at a strategic disadvantage relative to your competitors.
Opportunities are positive factors for your firm that arise from external contingencies. These could stem from technological change or macroeconomic developments. They could also come from legislative changes or mutations in your competitive landscape.
Threats like opportunities arise from external factors and will likely have the same, or similar, causes as listed above only with negative consequences for your business.
When to use SWOT?
Use SWOT when you want to:
- assess options for known problems
- identify emergent problems
- identify the most effective direction for your company
- assess your potential or your limitations
- …
Take out.
There are two main strategic responses once you have completed your analysis. Firstly, there is the attempt to match your strengths to the opportunities. In this way you can seek to gain a competitive edge over your rivals with respect to the prevailing business trends. The second option is convert or mitigate your threats or weaknesses, and in so doing protect yourself from potential downsides.


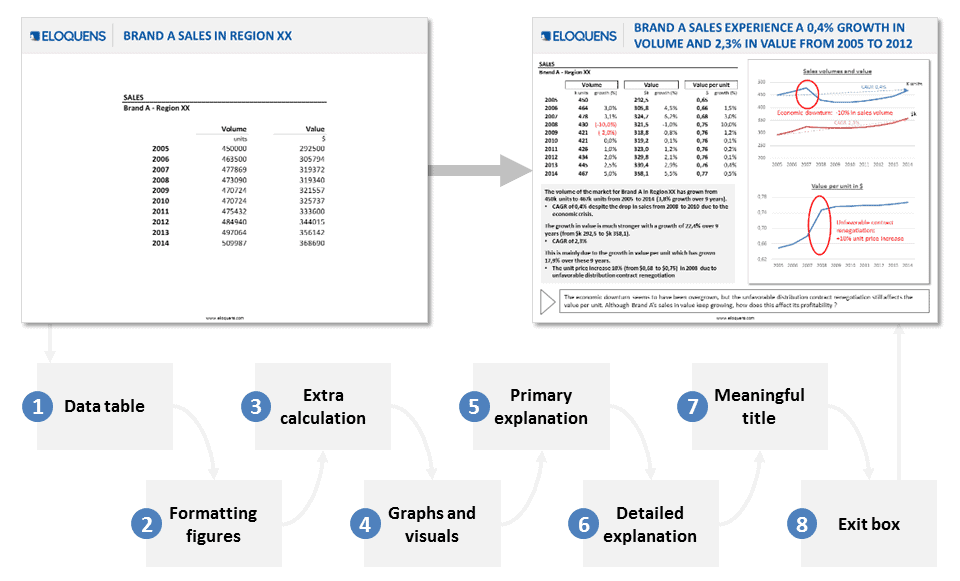







Basics, but efficient! And when you don’t know how to go about something, SWOT approach remains a good starting point!